Fill in a Valid Arizona 652 Template
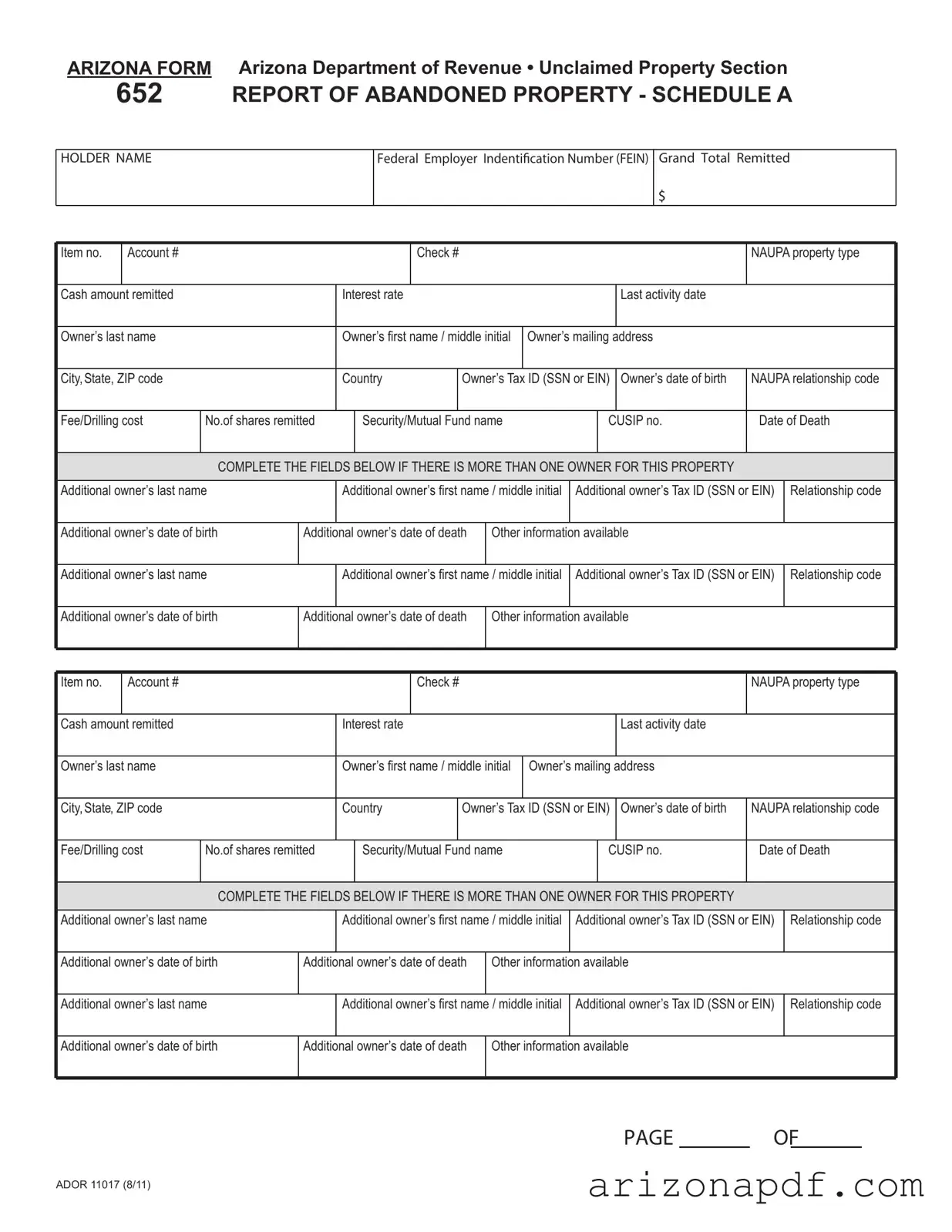
Navigating the complexities of unclaimed property in Arizona is a task made significantly easier with the introduction of the Arizona Department of Revenue Form 652, Report of Abandoned Property - Schedule A. This document serves as a critical tool for entities holding unclaimed assets to report them to the state, ensuring that these properties can be returned to their rightful owners. Form 652 carefully outlines the information required from holders, including the federal employer identification number, the total amount remitted, detailed information about the property such as account numbers, check numbers, types of property (under NAUPA property type codes), cash amounts remitted, and the last activity date. Importantly, it gathers comprehensive details about the owners, such as names, mailing addresses, tax IDs, birthdates, and if applicable, the date of death. The form even accommodates the reporting of multiple owners for a single piece of property, asking for additional owners' names, tax IDs, and other relevant details. Designed to streamline the process of reconnecting owners with their abandoned assets, the submission of this form is not only a compliance requirement but a crucial step in the responsible management of unclaimed property.
Arizona 652 Preview

ARIZONA FORM Arizona Department of Revenue • Unclaimed Property Section
652 REPORT OF ABANDONED PROPERTY - SCHEDULE A
HOLDER NAME
Federal Employer Indenti
Grand Total Remitted
$
Item no. |
Account # |
|
|
|
|
|
Check # |
|
|
|
|
|
NAUPA property type |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash amount remitted |
|
|
|
Interest rate |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Last activity date |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Owner’s last name |
|
|
|
Owner’s first name / middle initial |
Owner’s mailing address |
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
City, State, ZIP code |
|
|
|
Country |
|
Owner’s Tax ID (SSN or EIN) |
Owner’s date of birth |
NAUPA relationship code |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Fee/Drilling cost |
No.of shares remitted |
|
Security/Mutual Fund name |
|
|
CUSIP no. |
Date of Death |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
COMPLETE THE FIELDS BELOW IF THERE IS MORE THAN ONE OWNER FOR THIS PROPERTY |
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Additional owner’s last name |
|
|
Additional owner’s first name / middle initial |
Additional owner’s Tax ID (SSN or EIN) |
Relationship code |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Additional owner’s date of birth |
|
Additional owner’s date of death |
Other information available |
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Additional owner’s last name |
|
|
Additional owner’s first name |
/ middle initial |
Additional owner’s Tax ID (SSN or EIN) |
Relationship code |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Additional owner’s date of birth |
|
Additional owner’s date of death |
Other information available |
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item no. |
Account # |
|
|
|
|
|
Check # |
|
|
|
|
|
NAUPA property type |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash amount remitted |
|
|
|
Interest rate |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Last activity date |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Owner’s last name |
|
|
|
Owner’s first name / middle initial |
Owner’s mailing address |
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
City, State, ZIP code |
|
|
|
Country |
|
Owner’s Tax ID (SSN or EIN) |
Owner’s date of birth |
NAUPA relationship code |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Fee/Drilling cost |
No.of shares remitted |
|
Security/Mutual Fund name |
|
|
CUSIP no. |
Date of Death |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
COMPLETE THE FIELDS BELOW IF THERE IS MORE THAN ONE OWNER FOR THIS PROPERTY |
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Additional owner’s last name |
|
|
Additional owner’s first name / middle initial |
Additional owner’s Tax ID (SSN or EIN) |
Relationship code |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Additional owner’s date of birth |
|
Additional owner’s date of death |
Other information available |
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Additional owner’s last name |
|
|
Additional owner’s first name |
/ middle initial |
Additional owner’s Tax ID (SSN or EIN) |
Relationship code |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Additional owner’s date of birth |
|
Additional owner’s date of death |
Other information available |
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PAGE OF
ADOR 11017 (8/11)
File Properties
| # | Fact | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Form Designation | Arizona Department of Revenue Form 652 |
| 2 | Purpose | Report of Abandoned Property - Schedule A |
| 3 | Responsible Agency | Arizona Department of Revenue, Unclaimed Property Section |
| 4 | Governing Law(s) | Arizona Unclaimed Property Laws |
| 5 | Key Information Required | Holder name, federal employer identification, owner details, type of property, amount remitted, last activity date, etc. |
| 6 | Unique Features | Includes fields for both single and multiple owners of the abandoned property |
| 7 | NAUPA Codes | Utilizes the National Association of Unclaimed Property Administrators (NAUPA) property type codes |
| 8 | Submission Requirement | Mandatory for holders of abandoned or unclaimed property as specified by state guidelines |
| 9 | Accessibility | Form can be accessed through the Arizona Department of Revenue's website |
Instructions on Utilizing Arizona 652
Filling out the Arizona 652 form is a crucial step in the process of reporting unclaimed property. This form allows businesses and entities to report personal property that has gone unclaimed within the state of Arizona. It's a detailed document that requires attention to accuracy to ensure all appropriate information about the property and its owner is correctly communicated to the Arizona Department of Revenue. When completed, this form will assist in the process of potentially returning unclaimed property to its rightful owner or heirs. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you navigate the form.
- Start by entering the HOLDER NAME, which is the name of the business or entity holding the unclaimed property.
- Fill in the Federal Employer Identification (EIN) number of the holder.
- Enter the Grand Total Remitted, which represents the total cash amount of all items being reported.
- For each item of unclaimed property, start by entering the Item no. sequentially.
- Input the Account # associated with the unclaimed property.
- If applicable, fill in the Check # related to the unclaimed property.
- Select the appropriate NAUPA property type code from the provided guide that best describes the nature of the unclaimed property.
- Enter the Cash amount remitted, if the unclaimed property is in cash.
- If there is an Interest rate applicable, include that information.
- Document the Last activity date, which is the last date there was any owner activity on the account.
- Complete the owner's information, including last name, first name/middle initial, mailing address, city, state, ZIP code, and country
- Fill in the Owner’s Tax ID (SSN or EIN) and, if available, the Owner’s date of birth.
- Enter the NAUPA relationship code that describes the owner’s relationship to the property.
- If there are fees or drilling costs, include those amounts in the Fee/Drilling cost field.
- For securities or mutual funds, enter the No. of shares remitted, Security/Mutual Fund name, and CUSIP no.
- If the owner is deceased, include the Date of Death.
- If there is more than one owner, repeat the property and owner details in the section titled "COMPLETE THE FIELDS BELOW IF THERE IS MORE THAN ONE OWNER FOR THIS PROPERTY". Include additional owners' last names, first names/middle initials, Tax IDs (SSN or EIN), Relationship codes, dates of birth, and dates of death, if applicable. Add any other information available in the designated space.
Once you've filled out the Arizona 652 form with all the required information, review it carefully to ensure accuracy and completeness. Remember, this form is a legal document and inaccuracies may lead to delays or complications in the unclaimed property process. After reviewing, sign and date the form and follow the instructions for submission as provided by the Arizona Department of Revenue. By thoroughly and accurately completing this form, you play a vital role in the important process of reuniting owners with their unclaimed property.
Listed Questions and Answers
What is the Arizona 652 form used for?
The Arizona 652 form, crafted by the Arizona Department of Revenue, functions as a crucial document for reporting abandoned or unclaimed property. This includes, but is not limited to, unclaimed wages, bank account balances, and safety deposit box contents. Holders of such property, usually businesses or financial institutions, are mandated to file this form as part of their legal obligations to report personal property that has remained unclaimed by its rightful owner past a certain period.
Who is required to file the Arizona 652 form?
Entities such as financial institutions, corporations, associations, and insurance companies, among others, find themselves obligated to file the Arizona 652 form. This requirement kicks in when these entities hold property which has gone unclaimed. The law necessitates that they attempt to contact the rightful owner of the property within a specified timeframe. Failing to establish contact necessitates the filing of this form to report the unclaimed assets to the state, ensuring that efforts can be made to reunite the property with its legal owner.
What information do I need to complete the Arizona 652 form?
To correctly fill out the Arizona 652 form, detailed information regarding the unclaimed property and its owner is required. This includes the account number, the cash amount remitted, the last activity date, and information about the property's owner such as their name, mailing address, social security number or employer identification number, and date of birth. If there is more than one owner of the property, their details must also be reported on the form. Additionally, specific identifiers like the NAUPA (National Association of Unclaimed Property Administrators) property type and relationship codes are crucial for the proper categorization and processing of the unclaimed property.
Where do I file the Arizona 652 form and is there a deadline?
The Arizona 652 form should be submitted to the Unclaimed Property Section of the Arizona Department of Revenue. There is an annual deadline for submitting this form, typically by November 1st, to report unclaimed property based on the status of the property as of June 30th of that same year. It is imperative that institutions and businesses adhere to this deadline to ensure compliance with state law and to facilitate the timely return of unclaimed property to rightful owners. Late submissions can lead to penalties and interest charges, stressing the importance of timely and accurate reporting.
Common mistakes
Filling out the Arizona Form 652, which is related to the report of abandoned property, often involves a series of detailed steps. Despite the form's straightforward appearance, errors can occur. Identifying these mistakes beforehand can ensure a smoother process for individuals and organizations alike. Here are ten common mistakes:
Not including complete owner information, such as the full name and address of the property owner. This omission can lead to delays or even prevent the property from being properly claimed.
Incorrectly or incompletely filling out the account number or check number. These details are crucial for correctly identifying the property in question.
Using an incorrect NAUPA (National Association of Unclaimed Property Administrators) property type code. Selecting the wrong code can misclassify the type of property being reported.
Forgetting to include the cash amount remitted or entering an inaccurate amount. This figure is essential for the proper accounting and claiming of the funds.
Omitting the last activity date. This date helps determine when the property became dormant and eligible to be considered abandoned.
Failing to provide the property owner's Social Security Number (SSN) or Employer Identification Number (EIN), which is necessary for tax purposes and to confirm the owner's identity.
Leaving the owner's date of birth blank, especially important if the property belongs to an individual. This information is used to help verify the owner's identity.
Incorrectly reporting the number of shares remitted or the name of the security/mutual fund, which can lead to confusion or issues in the claiming process.
Not completing the additional owner sections when there is more than one owner for a piece of property. This can result in incomplete reporting and difficulties for co-owners attempting to claim their property.
Forgetting to specify the relationship code for the additional owner, which indicates the nature of their ownership or entitlement to the property.
By avoiding these mistakes, individuals and organizations can ensure their reports are accurate and compliant with Arizona's regulations, thereby aiding in the efficient return of property to its rightful owners.
Documents used along the form
When dealing with the Arizona 652 form, a Report of Abandoned Property, it’s important to have a comprehensive understanding of additional forms and documents that might be necessary to complete the process effectively. The Arizona 652 form is utilized by entities to report personal property that has been unclaimed by its rightful owner for a period, thereby transferring it to the state. This process not only requires meticulous attention to detail but also a collection of supplementary documents to ensure legal compliance and thoroughness.
- Cover Sheet for Report of Unclaimed Property (Arizona Form 650): This form acts as an introduction to the package of documents being submitted. It includes the holder’s information and a summary of the enclosed report, serving as a guide for state officials processing the unclaimed property.
- Holder Notification Letter: Before submitting the Arizona 652 form, a notification letter is usually sent to the presumed owner of the abandoned property at their last known address. This document is crucial as it demonstrates the holder's attempt to contact the owner before deeming the property as abandoned.
- Due Diligence Affidavit: This affidavit is a sworn statement verifying that the entity holding the unclaimed property has made all reasonable efforts to locate and notify the property’s owner. It acts as a legal testament to the due diligence performed prior to reporting the property as abandoned.
- Detailed Inventory List: Accompanying the Arizona 652 form, this list provides a detailed breakdown of all items being reported as unclaimed. This includes descriptions, values, and any identifying information that could aid in returning the property to its rightful owner.
- Power of Attorney (POA) Authorization: If the report of abandoned property is being filed by an agent or representative on behalf of the entity holding the unclaimed property, a POA authorization is necessary. This document grants the representative the authority to act on the holder’s behalf in matters related to the unclaimed property.
In summary, accurately completing and submitting the Arizona 652 form requires not only a careful review of the form itself but also an understanding and preparation of several additional documents. These documents work in concert to provide a thorough and legally compliant report of abandoned property, ensuring that every attempt has been made to return the property to its rightful owner and that the process is transparent and accountable. The collective effort to return unclaimed property reflects a broader commitment to fiscal responsibility and the protection of individual property rights.
Similar forms
The Arizona 652 form, known for its role in reporting abandoned property, shares similarities with the Uniform Unclaimed Property Act (UUPA) Holder Report Form. Like the Arizona 652, the UUPA form is utilized across various states for entities to report unclaimed properties. Both documents require detailed information about the holder, the property, and the owner, including names, addresses, and identification numbers. They play a crucial role in the process of returning lost or forgotten assets to rightful owners, ensuring compliance with state laws.
Another document similar to the Arizona 652 form is the IRS 1099 form. While the 1099 form is primarily for reporting income from various sources not involving wages, salaries, or tips, it parallels the Arizona 652 in its requirement for detailed financial and personal information. Both forms necessitate the provision of taxpayer identification numbers and personal details to ensure proper handling and reporting of financial data within the jurisdiction of tax and unclaimed property laws.
The SEC Schedule 13D is also akin to the Arizona 652 form in certain respects. This form is filed with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission by anyone who acquires more than 5% ownership of a publicly traded company. Similar to the Arizona 652, it requires detailed information about the owner, including personal information and the specifics of the ownership. Both documents serve to inform regulatory bodies and ensure transparency in financial and ownership transactions.
Furthermore, the FDIC Unclaimed Funds Form shares similarities with the Arizona 652. This form is used to claim funds from forgotten bank accounts insured by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation. Both the FDIC form and the Arizona 652 necessitate thorough details about the owner and the property, aiding in the rightful return of assets. They are vital tools for addressing issues related to unclaimed or abandoned funds.
The TreasuryDirect Form 1048, used for replacing or reissuing U.S. Savings Bonds, mirrors the Arizona 652 form in certain processes. It requires comprehensive information about the bond, the owner, and any co-owners, paralleling the detailed owner and asset information on the Arizona 652. These forms are instrumental in safeguarding assets and ensuring they are correctly attributed to their legal owners.
The SAFEKEEPING RECEIPT (SKR) is another document related to the Arizona 652 form. SKRs are used to prove the ownership and existence of valuable assets without physically transferring them. While serving a different primary purpose, both the SKR and Arizona 652 involve detailed recording of asset ownership, ensuring legal and rightful ownership is documented and recognized by relevant authorities.
Last, the Estate Tax Return (Form 706) shares a purposeful similarity with the Arizona 652 form in the aspect of reporting. Although Form 706 is specifically for reporting the estate of a decedent, it, like the Arizona 652, requires extensive documentation regarding the decedent's assets and their values. Both documents serve as vital links in the chain of asset transparency and legal compliance within their respective contexts.
Dos and Don'ts
Filling out the Arizona 652 form, the Report of Abandoned Property - Schedule A, is a critical task for those handling unclaimed assets. This form is utilized to report abandoned or unclaimed property to the Arizona Department of Revenue. While completing this document, it is essential to follow specific guidelines to ensure accuracy and compliance. Here are some dos and don'ts to consider:
- Do thoroughly review the form instructions before starting. Understanding what is required for each field can save time and prevent errors.
- Do ensure that all required fields are completed accurately. Incomplete forms can lead to processing delays or the rejection of your report.
- Do verify the accuracy of the Federal Employer Identification Number (EIN) and any other identification numbers to avoid misreporting.
- Do use the NAUPA (National Association of Unclaimed Property Administrators) property type codes correctly to categorize unclaimed properties appropriately.
- Do document the last activity date accurately. This date is crucial for determining when the property is considered abandoned or unclaimed.
- Don't estimate or guess information. If certain details are unknown, make efforts to obtain the accurate information before submission.
- Don't overlook additional owner details if applicable. When a property has more than one owner, failing to report all relevant information can lead to complications in reuniting the rightful owners with their property.
Following these guidelines will help ensure that the form is filled out correctly and efficiently, aiding in the smooth processing of unclaimed property reports. Accuracy and diligence are key in completing the Arizona 652 form to meet legal and procedural requirements.
Misconceptions
When it comes to handling unclaimed property in Arizona, the use of Form 652 is crucial. However, there are several misconceptions about this form and its requirements. Understanding these misconceptions can help individuals and businesses better navigate the complexities of unclaimed property reporting. Here's a closer look at some of these misunderstandings:
Only financial institutions need to file Form 652: This is not true. While banks and financial institutions might frequently deal with unclaimed property, Arizona law requires all entities, including businesses and organizations, that hold unclaimed property to report it using Form 652.
Reporting unclaimed property is optional: Many people think reporting unclaimed property is voluntary. However, in Arizona, holders of unclaimed property are legally obligated to report and remit this property to the state after a certain period, typically five years.
Form 652 is for reporting property within Arizona only: Although the form is filed with the Arizona Department of Revenue, it's a common misconception that only property belonging to Arizona residents must be reported. In truth, if the owner’s last known address is in Arizona, the property must be reported to the state, regardless of where the holder is based.
You can report any time of the year: Arizona has specific deadlines for reporting unclaimed property, generally April 30 for most property types. Waiting until after the deadline can result in penalties and interest.
Small amounts of unclaimed property don't need to be reported: Regardless of the amount, all unclaimed property must be reported. There is no minimum threshold that exempts property from being reported to the Arizona Department of Revenue.
Owner information is not crucial for reporting: On the contrary, providing comprehensive and accurate owner information, including their last known address and, if available, the Social Security Number (SSN) or Employer Identification Number (EIN), is essential for the proper handling and eventual return of the property to its rightful owner.
Electronic reporting is optional: Arizona prefers and, in some cases, requires electronic reporting for unclaimed property to streamline the process and ensure accuracy. Therefore, it's important to familiarize yourself with the electronic reporting methods specified by the Arizona Department of Revenue.
Once filed, there's no need to keep records: Holders must maintain records related to unclaimed property for a minimum of seven years after the report is filed. This documentation is crucial for verifying the accuracy of the report and may be requested by the state during audits or inquiries.
Clearing up these misconceptions about the Arizona Form 652 can help ensure that individuals and entities correctly report unclaimed property, thereby reducing the chance of errors or legal issues while aiding in the return of property to its rightful owners.
Key takeaways
Filling out the Arizona 652 form, known as the Report of Abandoned Property - Schedule A, is a crucial responsibility for entities in possession of unclaimed property. This process is managed by the Arizona Department of Revenue's Unclaimed Property Section. Here are key takeaways to ensure that the form is filled out accurately and effectively:
- Understanding the holder's obligation: Entities holding unclaimed property are required to report and remit this property to the Arizona Department of Revenue to comply with state laws.
- Completeness of information: It's vital to provide all requested details for each item of abandoned property, including descriptions, amounts, and owner information to expedite the process and avoid errors.
- Importance of accuracy: Ensure the accuracy of the Federal Employer Identification Number (FEIN), owner names, addresses, and all other information to prevent delays or mismanagement of property claims.
- Last known address: Include the owner's last known mailing address, which is crucial for the state to attempt to return the property to its rightful owner.
- Reporting detail: Itemized details about the property, including account numbers, property type codes (NAUPA property type), and the value of cash or shares remitted, must be clearly indicated.
- Owner identification: Owner's Tax Identification Number (either SSN or EIN), date of birth, and, if applicable, date of death are essential for identifying the rightful owner of the property.
- Multiple owners: If property has more than one owner, details for all owners must be completed, including names, Tax IDs, relationship codes, and dates of birth or death.
- Documentation and submission: After ensuring all information is complete and accurate, the form should be submitted in accordance with the Arizona Department of Revenue’s guidelines for reporting unclaimed property.
Adhering to these takeaways when filling out the Arizona 652 form helps in the efficient and lawful management of unclaimed property, ultimately facilitating the return of these assets to their rightful owners.
More PDF Forms
Az 285 - Ensures a secure and legally compliant process for authorizing representation in unclaimed property matters.
Making a Contract for Small Business - It outlines the terms and conditions regarding the sale of a commercial property, including purchase price and payment terms.
Paternity Test Arizona - The detailed instructions included with the form help guide parents through each step of the process to avoid common mistakes.